Pleural Mesothelioma vs. Lung Cancer
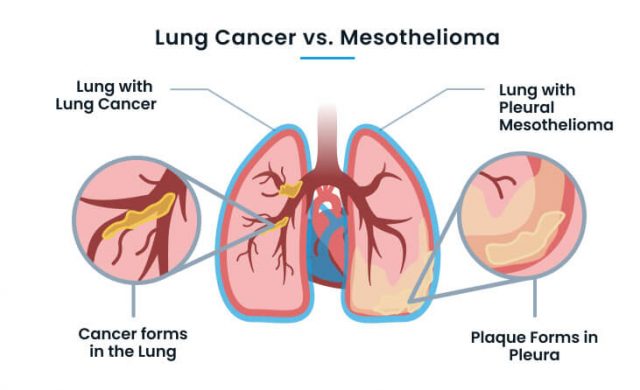
The difference between mesothelioma and lung cancer is how they affect the lung. Mesothelioma forms in the outer lining of the lung, while lung cancer forms in the lung tissue. Mesothelioma and lung cancer share similar symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue and weight loss.
Cancers in the Lining of the Lung
Though malignant pleural mesothelioma affects the lungs, it is not considered a type of lung cancer, because it forms in the lining around the lungs rather than in the lung tissue.
These cancers originate in different locations, yet cause similar symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue and weight loss. Symptoms tend to arise late in the development of both cancers.
Though medical teams use surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy to treat both conditions, the treatment plans differ, and what works for one cancer will not work for the other. Photodynamic therapy has been used on both, but it is more commonly used on lung cancer and is only experimental for pleural mesothelioma.
How Are Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Related?
These cancers share related staging systems. The early staging of both cancers is similar, but it differs in the latter stages as the cancer spreads.
Stage 1 and 2:
The tumors are localized, remaining where they originally developed.
Stage 3:
The tumors are locally advanced, meaning they’ve grown and spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes.
Stage 4:
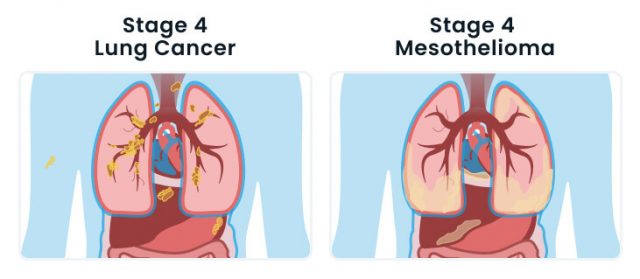
Lung cancer spreads throughout both lungs and to other parts of the body such as the brain, bones, liver and adrenal glands. Stage 4 mesothelioma less frequently spreads to distant locations, but may spread throughout both lungs or to the bones or brain.
Survival rates for these cancers are similar for the first year after diagnosis, but thereafter, lung cancer patients have better chances for long-term survival.
Less than 10 percent of pleural mesothelioma patients live for 5 years, according to the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program of the National Cancer Institute. Nearly 18 percent of people with lung cancer live that long.
What Is the Difference Between Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma?
While lung cancer and mesothelioma are both cancerous and arise from asbestos exposure, they differ in several meaningful ways. Among other differences, these cancers have separate origins in the body, defining tumor characteristics and distinct survival rates.
| Lung Cancer | Pleural Mesothelioma |
|---|---|
| Forms in lung tissue | Forms in the lining around the lungs |
| Common condition with more than 220,000 Americans diagnosed per year | Very rare with about 3,000 Americans diagnosed annually |
| Caused by smoking, air pollution and asbestos exposure | Caused primarily by asbestos exposure |
| Mainstream treatment options are surgery, chemotherapy and radiation | Also treated with surgery, chemotherapy and radiation but targeted differently |
| Tumors are well-defined masses that are easier to target for treatment | Tumors are thinly spread over healthy tissue, making them more difficult to target |
| 5-year survival rate: Almost 18 percent | 5-year survival rate: Less than 10 percent |
Diagnosing Mesothelioma & Lung Cancer
Doctors use similar diagnostic tools to identify these cancers, and the expertise of a specialist is required to differentiate pleural mesothelioma from lung cancer.
- X-ray: This is often the first test to show tumor growth around the lungs.
- CT or PET scan: Advanced imaging tests provide more detailed pictures of the inside of the chest and lungs.
- Biopsy: Collecting samples of cancerous tissue with a long needle or a minor surgery is essential to accurately diagnose the cancer.
- Sputum cytology test: If doctors suspect lung cancer, they can examine phlegm expelled by the patient.
- Bronchoscopy: Another common procedure for diagnosing lung cancer involves inserting a tube down the patient’s throat into the large airways to check for abnormal growths.
The most accurate and definitive method is to have a pathologist examine biopsy samples to decipher which cancer is present from a cellular level.
However, if the patient has a history of possible asbestos exposure, they should seek the opinion of a specialist in asbestos-related diseases. Pleural mesothelioma is sometimes misdiagnosed as lung cancer, because at the microscopic level, it can resemble adenocarcinoma, the most common type of non-small cell lung cancer. It can also resemble sarcoma, a cancer that forms in soft tissue.

Asbestos Increases the Risk of Lung Cancer
When microscopic asbestos fibers are inhaled, they can become lodged in lung tissue or the pleura, which is the lining of the lungs, and the mineral fibers can cause cancer in both locations. Asbestos lodged in lung tissue causes lung cancer, while asbestos lodged in the pleural lining causes pleural mesothelioma.
- All forms of asbestos, including amphibole and serpentine types, are known to cause lung cancer and pleural mesothelioma.
- Amphibole forms of asbestos (including amosite, crocidolite, tremolite and anthophyllite) are more carcinogenic than serpentine asbestos (chrysotile).
Regardless of the type of asbestos someone is exposed to, significantly less asbestos exposure is required to cause pleural mesothelioma than lung cancer.
In either case, it usually takes many years for asbestos exposure to cause cancer to develop. The average latency period for pleural mesothelioma is 10 to 50 years, while lung cancer’s latency period is shorter, at 10 to 20 years.
Smoking Doesn’t Increase the Risk of Pleural Mesothelioma
Asbestos exposure alone can cause both pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer, and smoking alone can cause lung cancer. However, smoking alone cannot cause pleural mesothelioma, and smoking doesn’t increase the risk of pleural mesothelioma in those exposed to asbestos.
- Studies have proven that the combination of smoking and asbestos exposure can increase the risk of lung cancer fiftyfold.
- Conversely, other research has proven that smoking does not affect the risk of developing pleural mesothelioma at all.
Because the toxic combination of smoking and asbestos exposure significantly increases the risk of lung cancer but not pleural mesothelioma, there are about twice as many cases of asbestos-related lung cancer in comparison to pleural mesothelioma.
It’s also worth noting that lung cancer risk decreases after smoking cessation, but the risk of pleural mesothelioma only increases with age. The body cannot recover from asbestos exposure the way it can from cigarette smoking — because asbestos fibers can become trapped in bodily tissues indefinitely, ongoing damage can carry on for decades. The risk of lung cancer may decrease with time and smoking cessation, but the risk of pleural mesothelioma only continues to increase.
Lung Cancer & Mesothelioma Treatment Plans
Common treatment options for mesothelioma and lung cancer are the same as for other cancers: Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. However, medical professionals treat pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer with distinct types of surgeries, chemotherapy drugs and radiation techniques because the two cancers form differently.
- Lung cancer tumors typically grow as individual masses, which makes them easier to surgically remove and target with chemotherapy and radiation.
- Mesothelioma develops as many small interconnected tumors that eventually blend the boundaries between healthy and cancerous tissue, making it much more difficult to target.
Different combinations of conventional treatments, known as multimodal therapies, are effective for each cancer, depending as well on the stage of the tumor and the overall health of the patient.
Surgery
Surgeries for lung cancer will attempt to remove either a portion of the affected lung, a lobe or the whole lung. Pleural mesothelioma surgeries may involve the removal of the pleural lining, a portion of the lung or the entire affected lung. Certain palliative surgeries, such as a pleurodesis, can provide pain relief in advanced cases of either cancer.
Only certain chemotherapy drugs are effective in treating pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer, and even then, the dose will depend on which cancer a patient has and the stage of the tumor.
Cisplatin and pemetrexed are the most common chemotherapeutic agents used for pleural mesothelioma, while docetaxel, vinorelbine and paclitaxel are common for treating lung cancer. Chemotherapy drugs used for both cancers include cisplatin, carboplatin, pemetrexed and gemcitabine.
Chemotherapy
Only certain chemotherapy drugs are effective in treating pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer, and even then, the dose will depend on which cancer a patient has and the stage of the tumor.
Cisplatin and pemetrexed are the most common chemotherapeutic agents used for pleural mesothelioma, while docetaxel, vinorelbine and paclitaxel are common for treating lung cancer. Chemotherapy drugs used for both cancers include cisplatin, carboplatin, pemetrexed and gemcitabine.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is difficult to administer to either cancer because of the proximity of the lungs to vital organs such as the heart and spinal cord. When administered alone, radiation aims to ease pain in pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer patients, but it cannot cure these cancers.
When combined with other treatments, especially following aggressive surgery, radiation therapy can reduce local tumor recurrence in pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer. For pleural mesothelioma patients, radiation has also been used along tracts created by biopsies, chest tubes and surgical incisions to prevent tumor seeding, or local metastasis along the incision. Tumor seeding is rare in lung cancer.
Other Treatments
Specialists have used photodynamic therapy to treat pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer, but it is more commonly administered to lung cancer patients. Researchers have used other novel treatments, such as immunotherapy and gene therapy, for both cancers with limited success so far.
Complementary and alternative medicine is available for both cancers and can ease mesothelioma symptoms as well as reduce side effects of conventional treatments.
Survival Rates for Lung Cancer and Pleural Mesothelioma
The prognosis for pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer is similar for the first year after diagnosis, but the survival rate for lung cancer is generally higher after five years.
| Extent of Cancer Spread | Lung Cancer | Pleural Mesothelioma |
|---|---|---|
| Localized | 60% | 18% |
| Regional | 33% | 11% |
| Distant | 6% | 7% |
Diagnosing the cancers early significantly improves survival rates.
Despite their similarities, pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer are separate conditions that require different treatment plans to extend survival. Patients with either cancer should work with a specialist who can offer expertise in the latest available treatments.
Mesothelioma Vs. Lung Cancer FAQ
- Is mesothelioma a type of lung cancer?
-
Mesothelioma is not a type of lung cancer. Pleural mesothelioma develops in the protective lining surrounding the lungs, while lung cancer develops inside lung tissue.
- What should I do if I suspect my lung cancer is actually mesothelioma?
-
If you are worried that you may have mesothelioma instead of lung cancer, you may seek a second opinion from a doctor specializing in mesothelioma. Sometimes mesothelioma is misdiagnosed as a form of lung cancer, but this is rare. A mesothelioma specialist can tell the difference.



